Mastering the Basics of Geo-Location Mobile Marketing: Powerful Examples and Emerging Trends

In today’s mobile-centric world, understanding the Basics of Geo-Location Mobile Marketing is essential for businesses aiming to engage with their audience in real-time. As smartphones have become a fundamental part of daily life, Geo-Location Mobile Marketing offers companies the ability to create personalized, location-specific campaigns that target users based on their geographic location. This strategy significantly enhances engagement, making it a powerful tool in the modern digital landscape.
This article will delve into the Basics of Geo-Location Mobile Marketing, how it works, real-world examples, and emerging trends that are shaping its future. Whether you are new to mobile marketing or refining your digital strategy, this guide will help you master the fundamentals of Geo-Location Mobile Marketing.
Table of Contents
1. The Basics of Geo-Location Mobile Marketing
Geo-location Mobile Marketing has revolutionized the way businesses interact with customers by using real-time geographic data. This approach allows for hyper-targeted ads, notifications, or content delivery to users based on their current location. By utilizing advanced technologies such as GPS, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth, companies can engage with users when they’re in proximity to stores, events, or landmarks. Imagine walking past a coffee shop and receiving a personalized push notification for a discount on your favorite beverage—this is the power of Geolocation Mobile Marketing in action. It leverages location data to create immediate and relevant interactions between businesses and consumers.
2. Key Concepts and Technologies in Geolocation Mobile Marketing
Understanding the core technologies and strategies that make this form of marketing successful is essential.
Geofencing
Geofencing is a technology that creates a virtual perimeter around a specific geographic area. When a user enters or exits this boundary, it triggers targeted messages, such as promotional offers or event updates. Retailers often use geofencing to attract foot traffic by delivering timely offers as potential customers pass by. For example, a department store might use geofencing to notify customers about a flash sale happening within the store.
How Does Geofencing Work?
Businesses set up a predefined geographic area using software. When a mobile device enters this area, a signal is sent, and the system triggers a message or action. This process makes marketing campaigns more dynamic, relevant, and context-sensitive.
Beacons
Beacons are small wireless devices that use Bluetooth technology to communicate with nearby smartphones and apps. They allow businesses to deliver hyper-targeted messages based on proximity. For example, a beacon placed at the entrance of a shopping mall can send a welcome message with store recommendations. Similarly, in a museum, beacons can provide visitors with detailed information about exhibits.
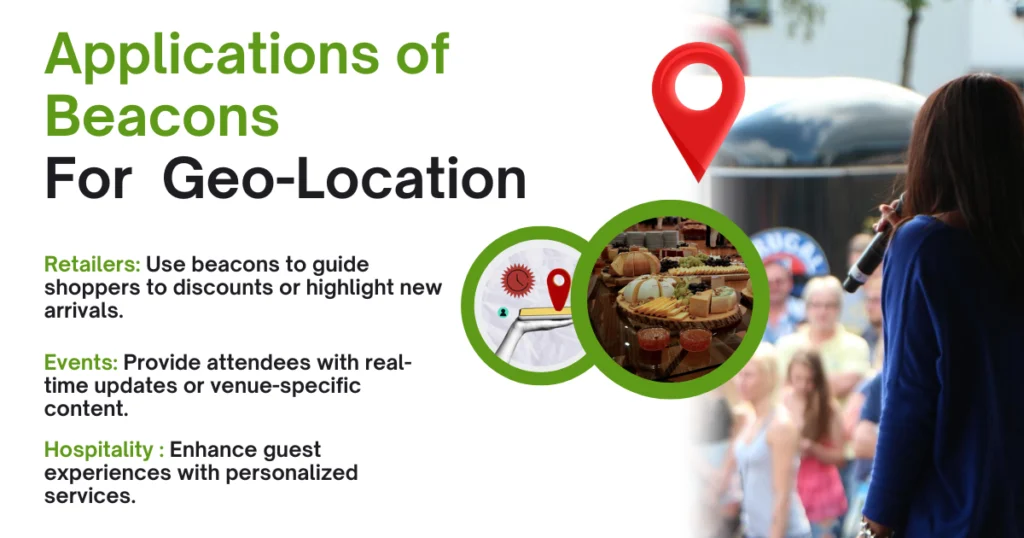
Applications of Beacons
Retailers: Use beacons to guide shoppers to discounts or highlight new arrivals.
Events: Provide attendees with real-time updates or venue-specific content.
Hospitality: Enhance guest experiences with personalized services.
Location-Based Services (LBS)
Location-Based Services use a user’s current location to deliver relevant content, whether it’s restaurant recommendations, nearby gas stations, or special offers. Mobile apps rely on LBS to provide tailored experiences, making users’ interactions more engaging and useful.
Examples of LBS in Action
Navigation Apps: Provide real-time directions and traffic updates.
Travel Apps: Suggest tourist attractions or accommodation nearby.
Dining Apps: Recommend top-rated restaurants in the area.
3. How Geolocation Mobile Marketing Works
The operation of Geolocation Mobile Marketing involves collecting and using location data to deliver personalized content to users.
- Identifying User Location: Using GPS, Wi-Fi signals, or Bluetooth, mobile devices provide precise location details.
- Triggering Messages: When a user enters a geofence or comes within the range of a beacon, the system activates and sends a notification or ad. This can be anything from a reminder about a loyalty program to a special offer.
- Delivering Targeted Content: Users receive content tailored to their current environment, increasing the likelihood of engagement.
This methodology ensures that marketing messages are well-timed and location-appropriate, enhancing user experience and business outcomes.
4. Benefits of Geolocation Mobile Marketing
Mastering Geolocation Mobile Marketing brings several advantages:
Personalization
Consumers are more likely to engage with personalized content. By using location data, marketers can tailor messages to specific user needs, preferences, and behaviors. Personalization increases user satisfaction and engagement rates.
Location-based marketing allows businesses to understand where their customers are at any given moment and deliver relevant marketing messages based on their physical location.
Increased Customer Engagement
Geolocation Mobile Marketing can significantly boost customer engagement by providing value at the right moment. For instance, if a user receives a discount offer while passing by a store, they are more inclined to visit immediately.
According to Factual, 9 in 10 marketers reported that location-based advertising generated higher sales.
Higher Conversion Rates
Because messages are targeted and timely, conversion rates for geolocation-based marketing campaigns are generally higher compared to generic advertising methods. When consumers receive relevant offers as they shop or explore a city, they are more likely to act on them.
Cost-Effectiveness
Traditional marketing campaigns often involve large budgets for broad reach, with no guarantee of impact. Geolocation Mobile Marketing, however, targets only those who are nearby and potentially interested, making it a cost-effective solution.
5. Real-World Examples
Starbucks and Location-Based Offers
Starbucks utilizes location data to drive foot traffic. When a customer is near a Starbucks outlet, the app sends a push notification featuring offers or new menu items. This personalized approach makes the brand’s marketing efforts feel relevant and timely.
Retail Stores Using Geofencing
Many retailers use geofencing to attract nearby customers. For example, a clothing store may set up a geofence around its vicinity and send push notifications for discounts or flash sales to potential shoppers in the area. This strategy can increase store visits and sales.
Uber’s Targeted Promotions
Uber’s geolocation strategy enhances user experience and engagement. During major events or in high-demand areas, Uber sends location-based ride promotions. For instance, if a large concert is happening, Uber might offer discounted rides to and from the event venue, attracting more users.
6. Emerging Trends
The landscape of Geolocation Mobile Marketing is evolving with technological advancements.
AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are making Geolocation Mobile Marketing smarter. These technologies analyze user behavior and location data to create predictive models, helping businesses anticipate consumer needs. For example, an AI-driven app might suggest a lunch spot just as the user starts feeling hungry, based on past behaviors.
Increasing Use of Beacons
As beacons become more sophisticated, their use is expanding beyond retail. Industries such as hospitality and healthcare are also exploring beacon technology to offer tailored experiences. For example, airports use beacons to guide travelers, and hotels use them to provide room service options.
Focus on Data Privacy
Data privacy concerns are shaping the way Geolocation Mobile Marketing is implemented. Transparency about data collection practices, opt-in mechanisms, and giving users control over their data are becoming critical aspects of marketing strategies.
The global location-based advertising market was valued at approximately USD 128.12 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.0% from 2025 to 2030.
7. Challenges and Considerations
Despite the benefits, there are challenges:
Data Privacy and Security
Collecting and using location data raises privacy concerns. Businesses must comply with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and ensure they handle user data responsibly. This includes obtaining explicit consent from users and providing options to opt out of data collection.
Battery Consumption
Geolocation features can drain a mobile device’s battery. Marketers must consider the impact of constant location tracking on user experience and find ways to minimize battery usage.
Accuracy of Location Data
Location data isn’t always 100% accurate. Factors like poor GPS signal in urban areas or incorrect Wi-Fi location can affect the precision of geolocation marketing campaigns. Businesses must account for these limitations in their strategies.
8. Cross-Channel Integration
Successful Geolocation Mobile Marketing often involves integration with other marketing channels:
- SMS and Push Notifications: These can be used to send geolocation-triggered alerts.
- Email Marketing: Location-based content can be included in email campaigns for better engagement.
- Social Media: Marketers can target ads based on users’ check-in locations and interests.
9. Future Outlook
The future of Geolocation Mobile Marketing looks promising, with innovations like:
- 5G Technology: Faster data speeds will improve the accuracy and effectiveness of location-based marketing.
- Wearable Devices: As wearables become more common, marketers will explore new ways to reach consumers through smartwatches and other gadgets.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR applications can provide interactive, location-based experiences, enhancing the impact of Geolocation Mobile Marketing.
Conclusion
Mastering Geolocation Mobile Marketing is crucial for businesses seeking to create engaging and personalized user experiences. By leveraging advanced technologies and staying updated on emerging trends, companies can deliver location-based content that drives engagement and conversions. As data privacy becomes increasingly important, businesses must also prioritize ethical practices to maintain consumer trust. With the right strategies, Geolocation Mobile Marketing can become a cornerstone of any successful mobile marketing campaign.




4 Comments
Comments are closed.